DevOps CI/CD Implementation
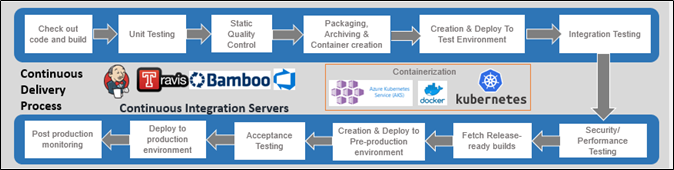
The Philosophy of Continuous integration (CI) is to make small code changes and check-in code frequently to a central repository and then ensuring that you are making progress in terms of features (or bug fixes) while not breaking any existing functionality. To be able to check if no existing functionality is broken is to check this frequently via automated tests. Thus, CI can meaningfully exist only when there is adequate automated testing.
Continuous Delivery (CD) starts its action where CI ends. The process of CD includes the automated delivery of applications to the assigned infrastructure environments. The DevOps teams work across multiple environments such as development, testing and production environments, and the CD process ensures there is an automated way to push code changes to these environments.
Thus, the practices of CI and CD typically embody a specific culture, a set of DevOps operating principles, and a collection of best automation practices that enables the development teams to deliver code changes more frequently and reliably. This specific implementation is known as CI/CD pipeline as the process ensures code quality and security as deployments are automated.
CI/CD practices requires continuous testing (CT) to ensure quality deployments as the basic objective of any project is to deliver quality software. This process of continuous testing is implemented using test automation tools with regression, performance, security, and other testing methods which are executed within the CI/CD pipeline.