Published: 09 Feb 2022
How to Overcome Challenges of Testing in Cloud Computing?
Last Updated: 01 Jul 2022
Cloud computing services or cloud infrastructure management have been gaining popularity and are considered one of the most disruptive forces in the IT industry. Today, enterprises are adopting cloud solutions as it helps them save money and effort that would otherwise be spent in maintaining and upgrading their on-premise infrastructure. Undoubtedly, cloud computing solutions are in more demand as they offer various advantages to businesses.
Content
1. What is cloud computing?
2. Major research analyst predictions on the cloud computing market
3. Types of cloud computing services
4. Some use cases of cloud computing
5. Major benefits for businesses with cloud computing
6. What is cloud testing?
7. Why should businesses leverage cloud testing?
8. Common testing challenges faced in cloud computing
9. How to overcome the challenges of testing in cloud computing?
10. An overview of various types of cloud testing
11. Conclusion
What is cloud computing?

Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery/access of computing resources such as applications, servers, data storage, networks, etc., over the internet. It works on the pay-as-you-go model and delivers hosted services on the internet. Today’s businesses are rapidly adopting cloud computing, and its dominance in the market is growing significantly.
Major research analyst predictions on the cloud computing market

According to Fortune Business Insights, the global cloud computing market is projected to grow from $250.04 billion in 2021 to $791.48 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 17.9% during the forecast period 2021-2028.
According to Statista, the worldwide public cloud computing market is growing and is expected to reach an estimated 482 billion USD in 2022. This encompasses business processes, platforms, infrastructure, software, management, security, and advertising services delivered by public cloud services.
Types of cloud computing services
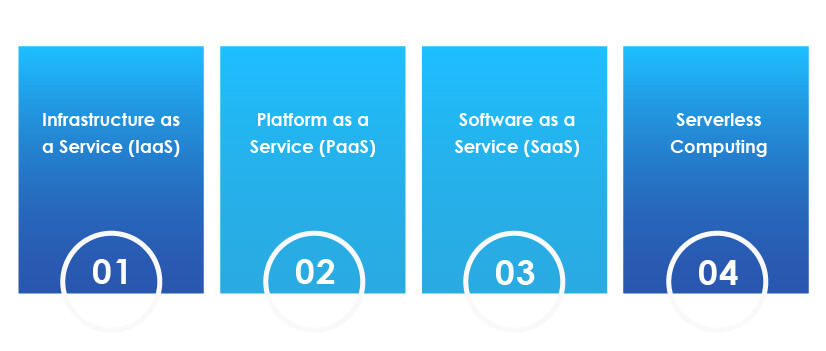
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
It allows users to rent physical, logical (network), and storage infrastructure from cloud vendors and deploys virtual machines on the cloud.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
It provides customers with a complete platform that includes hardware, software, and infrastructure required for developing, running, and managing applications.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
It provides ready-to-use software to clients over the internet. Instead of deploying, patching, and updating numerous apps on various devices, clients can quickly access SaaS applications over the internet.
4. Serverless Computing:
It is a cloud-based service where a cloud provider manages the servers and provides backend services on an as-used basis. It allows users to write and deploy code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Some Use Cases of cloud computing

1. Video streaming platforms:
Some on-demand video streaming apps include Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon Prime that leverage cloud computing and work on an on-demand streaming model.
2. File hosting services:
Most of the storage services that are designed to store data and create backup services are based on cloud computing models.
3. Chatbots/Voice assistants:
All major natural language intelligent chatbots/voice assistants, such as Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, etc., leverages cloud computing capabilities to provide human-like responses to customer queries. Cloud computing enables storing information related to user responses and preferences to provide a personalized experience.
4. Communication/collaboration apps:
Apps like calendars, Skype, emails, WhatsApp are all based on cloud models. All the messages and information are stored in the cloud to be accessed anywhere and anytime.
5. Backup and recovery tools:
All backup and recovery tools like Dropbox and Google Drive enable users to store data on the cloud rather than on-premise data storage centers. It ensures secure data storage, more storage space, and better data recovery options.
6. Social media apps:
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other social media apps utilize the power of cloud computing. The information shared by the user on these apps is stored in the cloud so that it can be accessed by the user anytime/anywhere and delivers a great user experience.
Major benefits for businesses with cloud computing
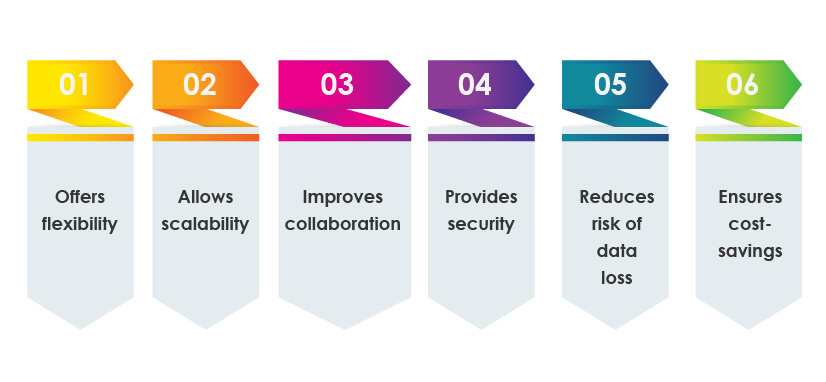
1. Offers flexibility:
Cloud computing provides great flexibility to users, as the data stored on the cloud is accessible from anywhere at any time.
2. Allows scalability:
Scaling the cloud computing services is very easy. If the user wants to buy extra storage space, the cloud provider can easily provide extra space by upgrading the package within a few minutes.
3. Improves collaboration:
Cloud computing services allow employees located at different places to collaborate easily. Employees can collaborate easily and work efficiently by simultaneously syncing, working, sharing the documents, and much more.
4. Provides security:
Storing data on the cloud is much safer than storing it on physical devices. As any breach of security in business premises can lead to loss of data, breaching the security of the cloud is not as easy as an on-premise breach due to the added layers of security.
5. Reduces risk of data loss:
Cloud computing services also reduce data loss chances. Cloud providers ensure data backup and recovery services that help users save their data without worrying about the potential risk of hackers, viruses, ransomware attacks, etc.
6. Ensures cost-savings:
Establishing and running the data center on-premise is expensive. Cloud computing cuts down the high cost of maintaining and updating hardware on-premise. Also, the pay-as-you-go model or the subscription-based model of cloud solutions saves businesses a lot of expenses and helps them also have access to automatic updates.
Cloud computing offers many benefits to businesses as data and services can be accessed anytime and from anywhere. But, businesses must leverage cloud testing to ensure their apps, infrastructure, and systems function seamlessly.
What is cloud testing?

Cloud testing, also known as cloud-based testing, includes testing an application in the cloud for performance, security, scalability, interoperability, multitenancy, etc. Typically, leveraging cloud computing infrastructure reduces the unit cost of computing and specifically increases testing efficiency. Cloud testing also provides compelling benefits of flexibility, scalability, testing complex test environments involving multiple mobile OS, browsers, various platforms, and much more.
Why should businesses leverage cloud testing?
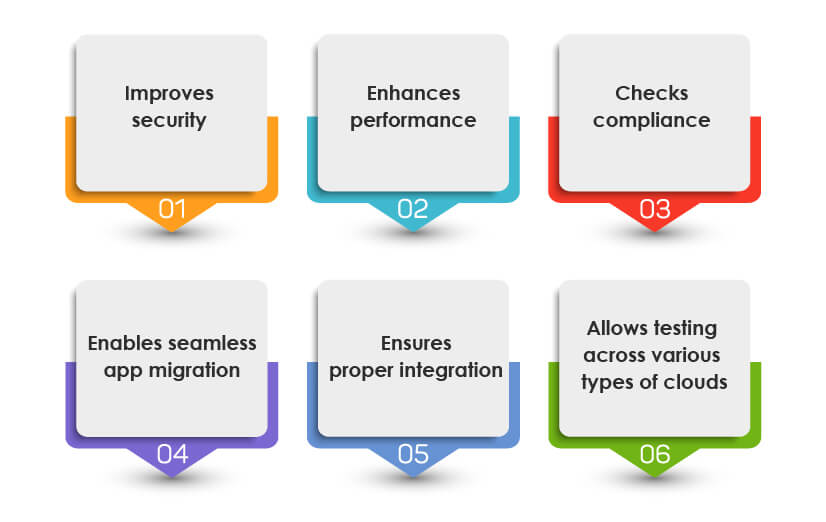
1. Improves security:
Cloud-based security testing is an effective way to improve the application’s security in the cloud. It ensures the identification of security loopholes and helps remove security vulnerabilities that cyber-attackers could otherwise exploit.
2. Enhances performance:
Performance testing in cloud computing ensures that there are no performance bottlenecks in the software and the auto-scaling features work properly so that servers or virtual machines can automatically manage the load handling capacity when traffic utilization levels fluctuate.
3. Checks compliance:
During cloud testing, testers also ensure that the application under test meets all the laws and regulatory compliance, such as data protection laws, data sovereignty laws, data localization laws, access to information laws, etc., necessary for an app to operate in the cloud.
4. Enables seamless app migration:
Cloud testing ensures effective migration of applications on the cloud by removing data migration issues related to incompleteness of migrated data, database errors, and other technical glitches.
5. Ensures proper integration:
Cloud testing removes the integration issues and ensures that the application is compatible with various platforms, properly integrates with servers, and works well in the cloud.
6. Allows testing across various types of clouds:
Cloud testing can be done across various types of clouds, such as public, private, hybrid, community, or their combinations.
Typically, the cloud computing environment also poses many challenges, and usually, these challenges tend to multiply with challenges of testing apps on the cloud. This cloud testing process involves testing apps across modules, and environments to identify various issues. Typically, businesses should understand and overcome these challenges to ensure their business-critical apps perform seamlessly and securely on the cloud.
Common testing challenges faced in cloud computing
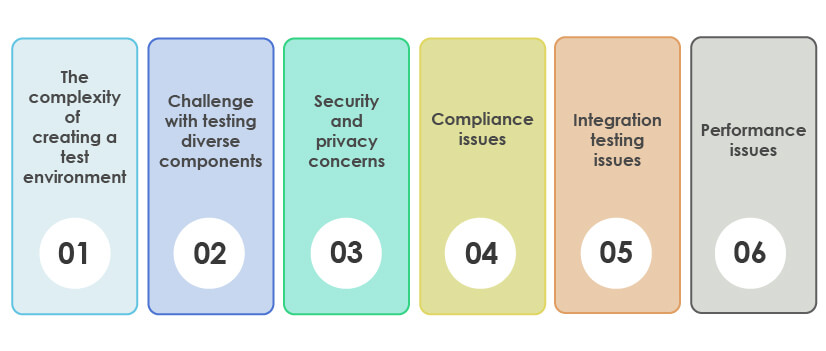
1. The complexity of creating a test environment:

One of the major challenges testers faces while testing in the cloud is creating a test environment containing all necessary app configurations and test data. Creating a test environment and managing the test environment is time-consuming and poses a significant challenge.
2. Challenge with testing diverse components:

Another challenge that testers face in cloud computing is testing diverse components that require the preparation of various test cases. The tester needs to identify the problem and prioritize the test cases, which consumes a lot of time and delays the delivery.
3. Security and privacy concerns:

Though cloud providers offer great security, data backup, and data recovery options, the risk of security breaches still exists. While conducting security testing manually, the testers can miss out on some security bugs; therefore, the chances of human-prone errors act as a great challenge for testers.
4. Compliance issues:

Compliance with legal regulations and standards is another challenge that cloud testers have to look at while testing in the cloud. Non-compliance of apps with these standards can lead to high penalties and sometimes even monetary and reputation loss.
5. Integration testing issues:

While performing the integration testing in the cloud, the test is performed on various components, such as network, database, systems, devices, servers, etc. Since testers have no control over the environment in the cloud testing, the chances of a database crash, any other breakdown, or server downtime might occur.
6. Performance issues:

If the network bandwidth offered by cloud services is low, it hampers the testing and delivery of apps in the cloud.
How to overcome the challenges of testing in cloud computing?

1. The challenge of creating a test environment can be overcome by leveraging cloud-based test environment management tools and frameworks, such as Testim.io., Plutora, etc.
2. The challenge of testing diverse components in the cloud can be overcome by leveraging automated cloud testing tools, such as Xamarin Test Cloud, Blaze Meter, LoadStorm, etc.
3. Testers should leverage automated cloud-based security testing tools such as Nessus, Acunetix, Metasploit, Nmap, etc., to overcome the challenge of security testing in the cloud.
4. Testers can overcome the challenge of compliance by creating a unique and comprehensive cloud test strategy to ensure compliance with standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.
5. Testers should leverage cloud-based integration testing tools, such as Rational Integration Tester, Protractor, SOASTA CloudTest, etc., to overcome the challenge of integration testing.
6. The challenge of app performance in the cloud can be overcome by leveraging cloud-based performance testing tools that work well under varying bandwidths. Some cloud-based performance testing tools are LoadView, LoadStorms, OctoPerf, Blazemeter, etc.
An overview of various types of cloud testing
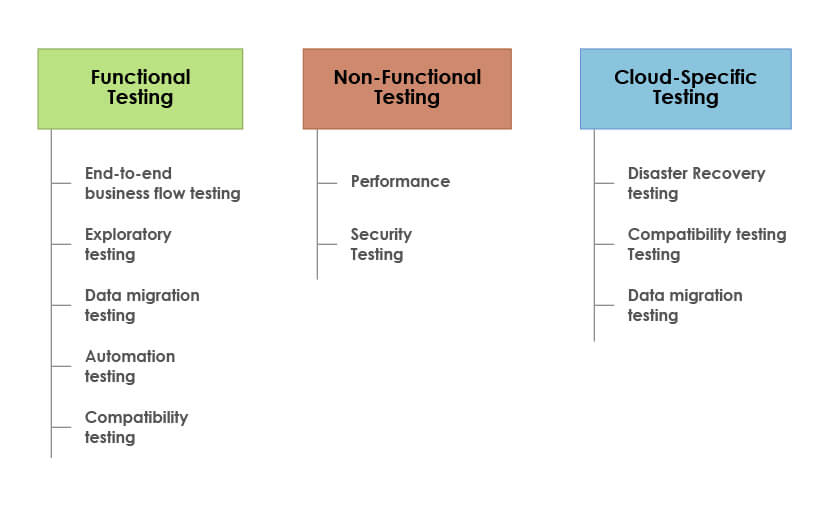
1. Functional Testing:
The main aim of this testing type is to ensure the application on the cloud functions seamlessly, meets all business needs and customer expectations. The various types of functional tests are:
End-to-end business flow testing: This testing method tests the application’s workflow from start to end. It involves real user scenarios to ensure the application works well and delivers a great CX.
Exploratory testing: In this software testing type, the application on the cloud is tested on the fly. The main aim of this testing type is to find bugs in the software quickly.
Data migration testing: As the name itself suggests, this testing type is performed to ensure proper data migration on the cloud. It ensures no data loss happens while data is migrated from various sources to the cloud.
Automation testing: This testing type involves automating end-to-end testing of the software. The main aim of this test is to speed up the software testing process, reduce regression testing time and find bugs more effectively.
Compatibility testing: This cloud testing type ensures the application is compatible with different platforms and works well when moved from one cloud infrastructure to another.
3. Non-functional Testing:
This cloud testing type validates the non-functional aspects of the software. The main aim of this test is to ensure high-performance, security, and reliability of the application on the cloud. Major non-functional testing types are:
Performance Testing: This test is performed to ensure the application effectively handles the high-user load and performs well under all conditions when moved to the cloud. It also involves load testing, scalability testing, availability testing, and volume testing.
Security Testing: This cloud testing type ensures end-to-end security of applications on the cloud. Applications, networks, and compliance are tested thoroughly in this testing type.
4. Cloud-specific testing:
This testing type is specially performed on the application in the cloud. It includes various testing methods:
Disaster Recovery testing: This test checks the disaster recovery time taken by the application and ensures the application becomes available to users again in minimum time with minimum or no data loss on the cloud.
Compatibility testing: This testing type is performed to ensure that the application in the cloud is compatible with various platforms, servers, networks in the cloud environment.
Multi-tenancy Testing: Multi-tenancy is an architecture where multiple tenants/users share the same physical resources of a single platform. This testing type is performed to ensure the software handles the high user load due to multiple tenants and ensures that tenants share proper resources with the underlying security.
Conclusion
Cloud solutions have gained significant importance in recent times and have become the need of the hour for enterprises. Businesses should ensure end-to-end testing of their apps in the cloud to reap the maximum benefits of cloud computing. However, some testing challenges in the cloud environment should be carefully handled and addressed. Businesses should leverage cloud testing from next-gen QA and independent software testing services providers for fully functional, high-performing, secure, and scalable cloud apps.